Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang University, ZJU-UIUC Institute, Interdisciplinary Center for Quantum Information, State Key Laboratory of Extreme Photonics and Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
2 Zhejiang University, ZJU-Hangzhou Global Science and Technology Innovation Center, Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro/Nano Electronic Devices and Smart Systems of Zhejiang, Hangzhou, China
3 Zhejiang University, Jinhua Institute of Zhejiang University, Jinhua, China
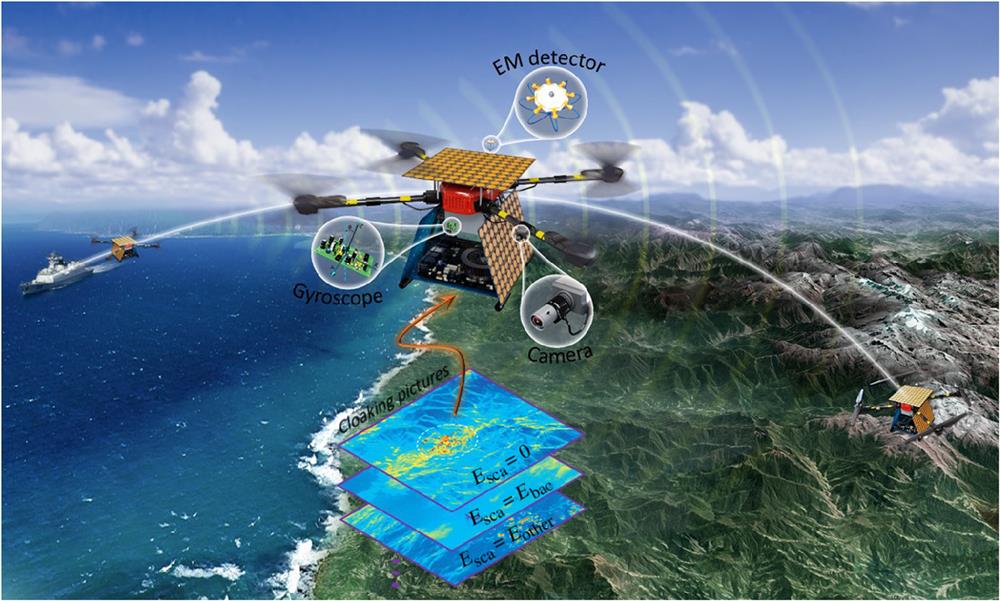
Being invisible ad libitum has long captivated the popular imagination, particularly in terms of safeguarding modern high-end instruments from potential threats. Decades ago, the advent of metamaterials and transformation optics sparked considerable interest in invisibility cloaks, which have been mainly demonstrated in ground and waveguide modalities. However, an omnidirectional flying cloak has not been achieved, primarily due to the challenges associated with dynamic synthesis of metasurface dispersion. We demonstrate an autonomous aeroamphibious invisibility cloak that incorporates a suite of perception, decision, and execution modules, capable of maintaining invisibility amidst kaleidoscopic backgrounds and neutralizing external stimuli. The physical breakthrough lies in the spatiotemporal modulation imparted on tunable metasurfaces to sculpt the scattering field in both space and frequency domains. To intelligently control the spatiotemporal metasurfaces, we introduce a stochastic-evolution learning that automatically aligns with the optimal solution through maximum probabilistic inference. In a fully self-driving experiment, we implement this concept on an unmanned drone and showcase adaptive invisibility in three canonical landscapes—sea, land, and air—with a similarity rate of up to 95%. Our work extends the family of invisibility cloaks to flying modality and inspires other research on material discoveries and homeostatic meta-devices.
intelligent metasurfaces optical materials and structures deep learning Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 016001
1 中国海洋大学信息科学与工程学部物理与光电工程学院青岛市光学光电子重点实验室,山东 青岛 266100
2 青岛科技大学数学物理学院,山东 青岛 266061
设计了一种可用于中红外波段探测的双层花瓣结构光学天线,利用有限时域差分方法,分析了结构参数、入射光偏振方向对单层天线共振波长及尖端电场强度的影响。在优化单层结构的基础上,计算了双层天线层间距(h)介于0.1~0.8 μm时,不同入射波长下上层天线尖端电场强度与入射光电场强度比值。为研究下层天线对于上层天线电场的增强机理,固定入射光波长,扩大天线层间距h(0.1~3.6 μm),对有无上层天线两种结构,分析相同探测点电场强度比随h的变化。结果表明,h<1 μm时,上层天线尖端电场增强主要来自于双层天线耦合增强,其中h<0.2 μm时,上层天线尖端场强随着距离h的减小而降低,主要因为近场耦合导致上层天线尖端能量转移到层间;h>1 μm时,上层天线尖端电场增强主要来自于下层天线反射光的干涉增强。
表面光学 光学天线 表面增强红外吸收 耦合增强 干涉 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(1): 0124001





